LC 00289: verschil tussen versies
Geen bewerkingssamenvatting |
Geen bewerkingssamenvatting |
||
| (10 tussenliggende versies door dezelfde gebruiker niet weergegeven) | |||
| Regel 1: | Regel 1: | ||
[[Bestand:Layer3_geentekst.jpg|gecentreerd|kaderloos|500x500px]] | |||
==== What is layer 3? ==== | |||
The third layer of the Multi-Layered safety concept refers to all temporary measures that can be taken in case of a actual flood threat. | |||
===== Layer 3 and the MLS concept ===== | |||
By using the Multilayered Safety (MLS) concept, different types of flood management measures are integrated, resulting in an overall reduction of the probability and the consequences of floods. MLS consists of four layers. Prevention is the first layer of MLS. The second and third layers are consequence-reducing measures, namely spatial solutions (layer 2) and preparedness and response (layer 3). Layer 1 and layer 2 are physical measures, whereas the third and fourth layers, crisis management and recovery, concentrates on organizational measures.Together, these layers can be tailored to local areas in order to minimize flood damage. | |||
[[Bestand:4layer illustratie totaal.jpg|gecentreerd|kaderloos]] | |||
==== What measures were taken in the FRAMES pilots in this layer? ==== | |||
{{Internal link|link=LC 00262|name=Preparedness and emergency planning|dialog=process-linkpage-dialog}} aims to support vulnerable people and areas susceptible to flood damage. This implies active risk communication by increased public awareness and preparedness and emergency response via contingency planning. | |||
{{Internal link|link=LC 00330|name=Community resilience|dialog=process-linkpage-dialog}} is both a function of the collection of individuals who comprise it and emergent properties that are dependent on social capital, social/cultural values, and practices, including duties to family members, the role of authorities within the community, trust, level of engagement and ethical norms ({{Cite|resource=Resource Hyperlink 00714|name=Etkin, 2016|dialog=process-linkwebsite-dialog}}). | |||
==== What tools were used in the FRAMES pilots in this layer? ==== | |||
| | FRAMES has compiled a list of tools used in the pilots and classified these per layer. Click {{Internal link|link=LC 00223|name=here|dialog=process-linkpage-dialog}} to find out what tools are available for layer 3. | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |||
{{Light Context | {{Light Context | ||
| Regel 42: | Regel 20: | ||
|Supercontext=PR 00274 | |Supercontext=PR 00274 | ||
|Topcontext=PR 00069 | |Topcontext=PR 00069 | ||
|Heading= | |Heading=Layer 3: Preparedness and response | ||
}} | }} | ||
Huidige versie van 8 jul 2020 om 14:27
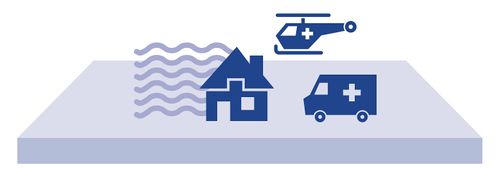
What is layer 3?
The third layer of the Multi-Layered safety concept refers to all temporary measures that can be taken in case of a actual flood threat.
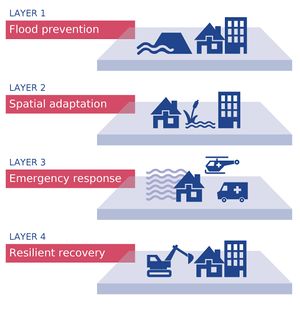
Layer 3 and the MLS concept
By using the Multilayered Safety (MLS) concept, different types of flood management measures are integrated, resulting in an overall reduction of the probability and the consequences of floods. MLS consists of four layers. Prevention is the first layer of MLS. The second and third layers are consequence-reducing measures, namely spatial solutions (layer 2) and preparedness and response (layer 3). Layer 1 and layer 2 are physical measures, whereas the third and fourth layers, crisis management and recovery, concentrates on organizational measures.Together, these layers can be tailored to local areas in order to minimize flood damage.
What measures were taken in the FRAMES pilots in this layer?
Preparedness and emergency planning aims to support vulnerable people and areas susceptible to flood damage. This implies active risk communication by increased public awareness and preparedness and emergency response via contingency planning.
Community resilience is both a function of the collection of individuals who comprise it and emergent properties that are dependent on social capital, social/cultural values, and practices, including duties to family members, the role of authorities within the community, trust, level of engagement and ethical norms (Etkin, 2016).
What tools were used in the FRAMES pilots in this layer?
FRAMES has compiled a list of tools used in the pilots and classified these per layer. Click here to find out what tools are available for layer 3.
Referenties
- Etkin 2016, Etkin, D., 1 januari 2016.
Hier wordt aan gewerkt of naar verwezen door: Adaptive planning, Community resilience, Critical infrastructure, Flood proof design and planning, Layer 3- Preparedness and response, Natural flood management, Preparedness and emergency planning, Recovery learning